Understanding Immunity and Aging
Overview
As people age, they often notice a decline in their immune’s effectiveness, leading to more frequent illnesses and slower recovery times. This summary explores the reasons behind this decline, its implications, and actionable steps to maintain a robust immune system.
The Aging Immune System
Decline in Immune Function
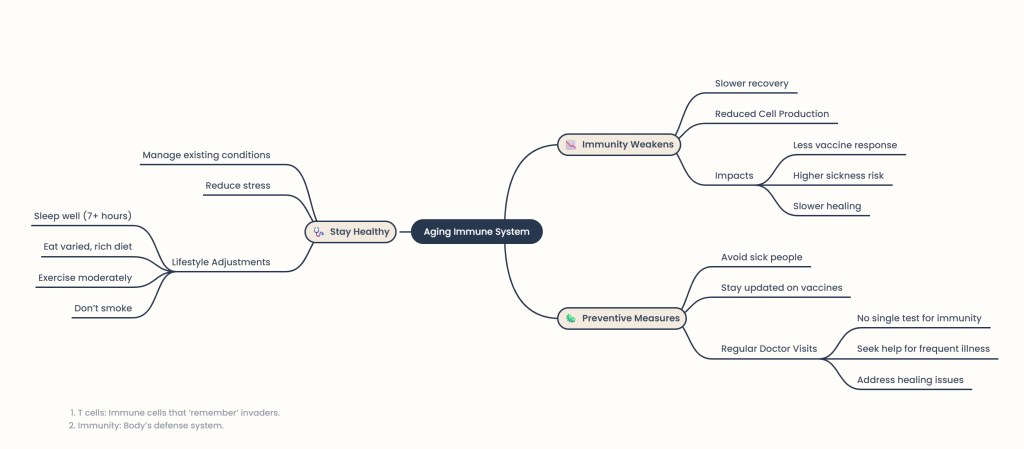
Aging Effects: Just as physical abilities diminish with age, the immune system also experiences a decline. Dr. Aaron E. Glatt notes that while the immune system may not function as well as it did in younger years, it still performs adequately for most individuals.
Research Insights: Dr. Kira Rubtsova highlights that the medical community is still investigating the exact mechanisms of how aging affects immunity. Key observations include:Older adults have a diminished response to vaccines due to fewer T cells, which are crucial for immune memory and response.
Communication between immune cells weakens, leading to slower reactions to infections.
Healing processes are prolonged due to a decrease in the production of immune cells, including white blood cells.
Individual Variability
There is no specific age at which immunity begins to decline; it varies from person to person, similar to the onset of gray hair. Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor immune health.
Strategies for Maintaining Immune Health
Regular Health Monitoring
Doctor Visits: Regular consultations with healthcare providers are vital, especially for individuals experiencing frequent illnesses or slow recovery from injuries.
Lifestyle Modifications
Manage Chronic Conditions: Proper management of conditions like diabetes and arthritis can alleviate stress on the immune system.
Prioritize Sleep: Aim for at least 7 hours of quality sleep each night, as poor sleep negatively impacts immunity. Consult a doctor if sleep issues arise.
Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can weaken immune responses. Techniques to manage stress can improve overall health and immune function.
Avoid Germ Exposure: Older adults should be cautious around sick individuals and practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing.
Stay Vaccinated: Keeping up with vaccinations is crucial, even if they are less effective in older adults. Vaccines can significantly reduce the risk of severe illnesses.
Exercise Regularly: Moderate physical activity can enhance immune function and improve cell mobility.
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports immune health. Focus on consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Quit Smoking: Smoking compromises immune function and increases susceptibility to infections. Seek assistance for cessation if needed.
While aging naturally affects the immune system, there are numerous proactive steps individuals can take to maintain and enhance their immune health. Regular medical care, a healthy lifestyle, and preventive measures can significantly contribute to a stronger immune response, helping older adults stay healthy and resilient.
