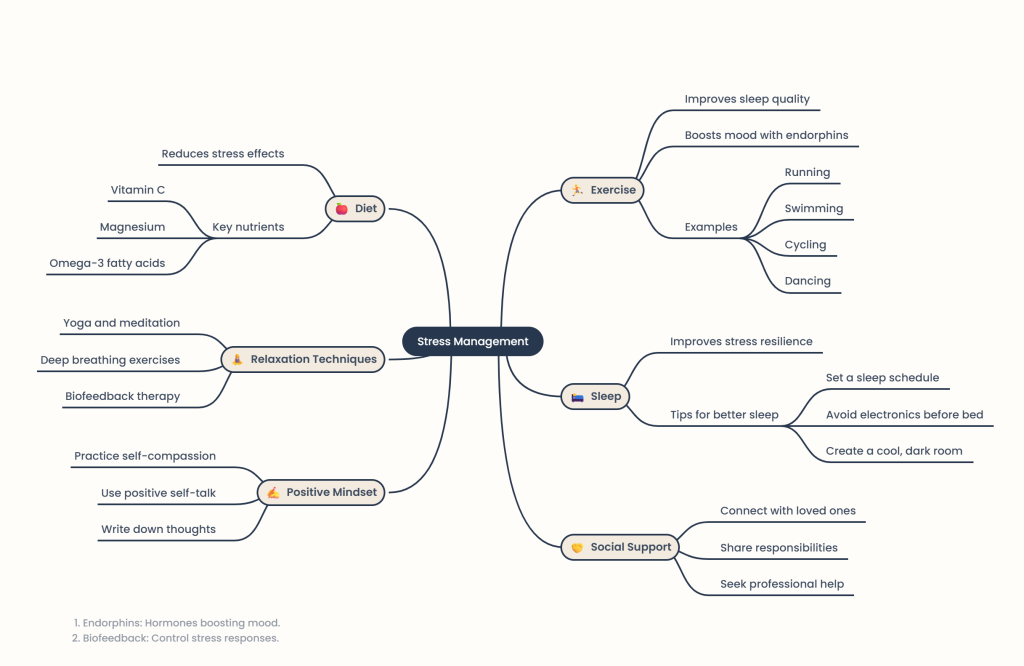
Summary of Stress Management Strategies
Stress is a natural aspect of human life, often serving as a motivator. However, prolonged stress, particularly from significant life events, can lead to feelings of anxiety and depression. It’s essential to seek professional help if these feelings persist for several weeks or interfere with daily life. Below are strategies and lifestyle changes to help manage stress effectively.
Understanding Stress
Normalcy of Stress: Stress can arise from various sources, including illness, job loss, and personal loss. Feeling down or anxious temporarily is normal.
When to Seek Help: Consult a doctor if feelings of anxiety or depression last longer than a few weeks or disrupt daily functioning.
General Stress Management Tips
Maintain a Positive Attitude: Focus on the positive aspects of life.
Accept Uncontrollable Events: Recognize that some situations are beyond your control.
Be Assertive: Communicate your feelings and needs without aggression.
Time Management: Learn to prioritize tasks and set limits to avoid excessive stress.
Engage in Hobbies: Make time for activities that bring joy.
Avoid Substances: Do not rely on alcohol or drugs as coping mechanisms.
Seek Social Support: Spend time with loved ones for emotional support.
Professional Help: Consider therapy or stress management training.
Lifestyle Changes for Stress Management
Physical Activity
Exercise Benefits: Regular physical activity can improve sleep, enhance mood, and reduce anxiety. It stimulates the release of endorphins and other hormones that promote well-being.
Types of Exercise: Running, swimming, dancing, cycling, and aerobics are effective stress relievers.
Incorporating: Find small ways to be active throughout the day, such as biking for errands or taking the stairs.
Nutrition
Healthy Eating: A balanced diet can mitigate stress effects. Focus on complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Nutritional Tips: Include antioxidants and specific nutrients like C, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids in your diet.
Avoid Processed Foods: Limit sugar and junk food intake, especially when stressed.
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep Issues: Stress can lead to insomnia, which in turn increases stress levels.
Improving Sleep: Establish a sleep routine, limit screen time before bed, and create a comfortable sleep environment.
Relaxation Techniques
Yoga and Meditation
Yoga: Combines physical exercise with meditation, focusing on deep breathing and slow movement to reduce anxiety.
Meditation: Involves focusing attention to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Deep Breathing
Practice Techniques: Engage in deep breathing exercises to activate the body’s relaxation response.
Biofeedback
Understanding Body Responses: Biofeedback helps individuals learn to control physiological responses to stress.
Social Connections and Behavior
Connect with Others: Spending time with friends or family can lower stress levels.
Behavioral Responses: Manage stress by avoiding overcommitment, taking a moment before responding, and distracting yourself with enjoyable activities.
Positive Thinking and Laughter
Inner Voice: Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations to improve stress resilience- Laughter Therapy: Engaging in laughter can boost mood and reduce stress through physiological benefits.
Professional Support
Talk Therapy: Long-term therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, can help individuals change negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies.
By implementing these strategies and lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage stress and improve their overall well-being.